Explanation
In this question, the zeroes on the top of the fraction
are a little different than under the fraction, because the zeroes in the
numerator do not repeat. So we can write
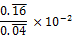
To simplify the fraction, forget about the horizontal bars
for a second. The fraction ![]() is 4. The fraction
is 4. The fraction ![]() is also 4. And so on. Since both the 16 and
the 04 are infinitely repeating in equal measure, the fraction is just 4. So
is also 4. And so on. Since both the 16 and
the 04 are infinitely repeating in equal measure, the fraction is just 4. So
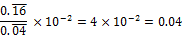
The correct answer is (A).
A final note: you may be surprised to hear that the
decimals above can be converted into fractions. You may be aware that a digit
over 9 equals that digit repeating in decimal form: ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
and the classic example,
,
and the classic example, ![]() .
Note that
.
Note that ![]() is the same as
is the same as ![]() .
In fact, any two-digit number over 99 is that two-digit sequence repeating. So
the fraction
.
In fact, any two-digit number over 99 is that two-digit sequence repeating. So
the fraction ![]() is
actually
is
actually ![]() divided by
divided by ![]() .
The 99's cancel, and we are left with
.
The 99's cancel, and we are left with ![]() .
No GMAT question will ever expect you to know this fact, but it can be handy
occasionally (and division by 9 is quite likely to come in handy at least once
on test day) when trying to simplify computations.
.
No GMAT question will ever expect you to know this fact, but it can be handy
occasionally (and division by 9 is quite likely to come in handy at least once
on test day) when trying to simplify computations.
Again, the correct answer is (A).
If you believe you have found an error in this question or explanation, please contact us and include the question title or URL in your message.